Topic: Symmetry
Instruction:
1- Each student is given a sheet of paper of different shape
2- Find a partner (any student in the classroom) of the same shape as yours.
3- As a whole class, use the shape that you have to come up with this:
Note:
1- Symmetry is a big word for primary school students.
2- Therefore, they need to learn it by hands-on activity.
3- This activity is to introduce the concept of symmetry, or to reinforce students' memory on shapes
Thursday, October 14, 2010
Statistics and Probability
Statistics refers to the process of collection, organization and interpretation of data. During the workshop, I was using Smarties to understand this concept. The data that I had collected was based on the colour of Smarties that each student has.
Firstly, I collected from each person the number of Smarties that they have according to color. There are pink, blue, yellow, green, red, brown and purple.
Secondly, based on the data collected, I knew the exact amount of each colour and I drew a bar graph on the magic board.
Finally, I was able to make some interpretation such as green and red colour have the most amount of all the colour and pink is the fewest. Whereas, blue and purple share the same amount.
Probability is the number of ways that an event can occur.
An example of probability. At the end, all has the same probability to reach which is 1.
Firstly, I collected from each person the number of Smarties that they have according to color. There are pink, blue, yellow, green, red, brown and purple.
Secondly, based on the data collected, I knew the exact amount of each colour and I drew a bar graph on the magic board.
Finally, I was able to make some interpretation such as green and red colour have the most amount of all the colour and pink is the fewest. Whereas, blue and purple share the same amount.
Probability is the number of ways that an event can occur.
An example of probability. At the end, all has the same probability to reach which is 1.
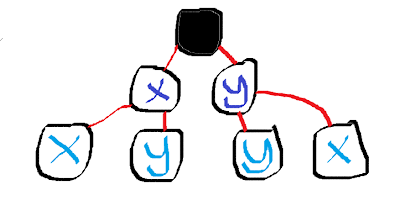
(A) X-X (B) X-Y (C) Y-Y (D) Y-X
This second example display how at the end they have a different probibility.
(A) X-X (B) X-Y, Y-Y (C) Y-X
(I regret that I did not capture even one photo of what I had done in the workshop. )
Wednesday, October 13, 2010
Geometry
Geometry is a branch of mathematics concerned with subject of shape, size, space and position. Points, line, symmetry and circle are the common things found when this subject is discussed.
Shape
There are many objects in our life that have similar shapes. Books, dictionaries, televisions, computers and papers are of the same shape - rectangle. Balls, water melons, oranges and tomatoes are round. Water bottle and bananas are cylinder.
During the workshop with Anne, we had come up with a village using papers. We created road, houses, buildings and junction using papers by designing many different shapes.
Shape
There are many objects in our life that have similar shapes. Books, dictionaries, televisions, computers and papers are of the same shape - rectangle. Balls, water melons, oranges and tomatoes are round. Water bottle and bananas are cylinder.
During the workshop with Anne, we had come up with a village using papers. We created road, houses, buildings and junction using papers by designing many different shapes.
the village in the making..
Symmetry
When a shape can be folded to become another shape, that is symmetry. For example, a rectangle can be folded into two shape. Thus, we consider a rectangle to have two symmetry.
In the workshop, we had the opportunity to try finding how many symmetry the shapes have using a mirror. If the mirror reflects the same shape, so it is symmetry.
Symmetry is a big word for young learners, therefore the introduction of the word should be accompanied by interesting activities. There are many suggestion of activities that teachers can carry out here
Tangrams
Tangram is a puzzle consisting seven flat shapes which can be put together to form shapes. The shapes are rectangle, triangle, parallelogram and trapezium.
a parallelogram
a triangle
a rectangle
Teacher tip-tops:
1- This topic really needs to be done using hands-on activity or games. There is no point for teachers to put more emphasis on explaining the meaning of any words used in the topic. Thus, teacher should prepare a range of activity to reinforce students' understanding.
2- Paper is the most suitable material to cater for all students' need in a lesson of this topic. Students can explore the concept of shape, symmetry and tangram using paper.
Measurement: Standard Unit
The second part of measurement is to use standard unit measurement. Standard unit measurement refers to definite magnitude of a physical quantity defined by conventional law and used as a standard measurement by people.
We, people, engage with lot of standard unit measurement in our everyday life. For instance, using money at shopping mall, weighting our weight in the gymnasium, determining the volume of ingredient we put when we bake a cake and look for the distance between our current location and destination that we head to.
measurement is important in preparing the ingredient to bake a cake
Given all these situations, it is no doubt that children should be exposed to the concept of measurement in school.
Standard unit measurement encapsulate concept of mass, weight, time, distance, length, weight, height, volume, area, perimeter and money. Each concept has different measurement units and measurement materials.
For example, we use meter, centimeter and millimeter for length and perimeter. For time, there are seconds, minutes and hour or even further day, week, fortnight, month, year and decade. Gram, kilogram and milligrams are the units for mass.
today, almost every house own this to measure their weight
this is normally used by tailor to measure their customers' body parts
ruler, very commonly used by students in school
Teacher tip-tops:
1- To have an understanding, repetition is important but the challenge is to make the repetition not a boredom. Off course, students will find it redundant to measure the same thing in the classroom. Thus, teachers' creativity is needed to provide students with array of opportunity to practice. For example, getting students to work outside the classroom or with people around the school. For example, ask the students to get weight of 20 people or measure the area of many places around the school.
2- Again, teachers should not limit students' curiosity to explore on their own by giving too many rules and instruction. Task-based learning can be employed in giving the students opportunity to 'play' with the concept. The tasks should be made to be general so that students can think on their own. For example, teachers ask the students to come up with ten function of a ruler and show how they use it.
Measurement: Non-standard
Measurement is the process of estimating or determining the quantitative value of any objects. Measurement is always connoted with mass, weight, height, volume and area. The ability of children to use the specific measuring items should be preceded by the ability to measure using things around their life.
Non standard measurement before standard measurement
Non standard measurement advocates the manipulation of classroom materials, natural material, body parts or classroom furniture to measure. This type of measurement should emphasize the development of comparative language such as 'more than', 'less than', 'bigger/ smaller than' and 'taller/ shorter than'.
This reflects the way people in the olden days (hundred years ago) measure things. They were manipulating their feet and hand to measure the area of their land, using the gap between sunrise and sunset to know how long they had been to work or even using containers of the same size to divide things among them.
In the workshop with Anne, we had the opportunity to measure many things using non-standard unit.
For example, using the area of a table to measure the area of the white board. We were using butch papers to represent the table and pasting the papers on the white boards. Finally, we discovered that the white board is equal to 12 tables.
We also tried to measure our body parts - height, hand, body and nose - using paper clips, unifix cubes, paddle pop sticks, straws. It was interesting to know the difference of measurement among us.
Also, we use pendulum to measure the time to construct a unifix tower of ten cubes. We found out that the times taken to completely construct a unifix tower differ as the length of the string changes.
Teacher tip-tops:
1- In setting up the area for teaching and learning measurement, teachers can either have one area to store all the materials in measurement or different areas for different types of materials. Also, restoring some materials of different types in a box is also interesting so that students can bring the box to where they want to measure things (especially outside the classroom). It works like a kit box.
2- Provision of opportunity for students to self explore the measurement materials before directed activities. However, guidance is still a necessity by giving questions like "I wonder if..." or "How many ways..". If students are able to produce or bring or think of an item to be measurement material, they should be used in classroom and shared among the class.
3- Directed activities are still prevalent but without too many instruction and rules which can limit their creativity and curiosity. Teachers should always give time for the students to explore and understand the concepts on their own as this will result in great insights.
Non standard measurement before standard measurement
Non standard measurement advocates the manipulation of classroom materials, natural material, body parts or classroom furniture to measure. This type of measurement should emphasize the development of comparative language such as 'more than', 'less than', 'bigger/ smaller than' and 'taller/ shorter than'.
is bigger than
using feet to measure length of an object e.g. land, wall, floor, etc.
In the workshop with Anne, we had the opportunity to measure many things using non-standard unit.
For example, using the area of a table to measure the area of the white board. We were using butch papers to represent the table and pasting the papers on the white boards. Finally, we discovered that the white board is equal to 12 tables.
We also tried to measure our body parts - height, hand, body and nose - using paper clips, unifix cubes, paddle pop sticks, straws. It was interesting to know the difference of measurement among us.
Also, we use pendulum to measure the time to construct a unifix tower of ten cubes. We found out that the times taken to completely construct a unifix tower differ as the length of the string changes.
use pendulum to measure time taken for an activity
Teacher tip-tops:
1- In setting up the area for teaching and learning measurement, teachers can either have one area to store all the materials in measurement or different areas for different types of materials. Also, restoring some materials of different types in a box is also interesting so that students can bring the box to where they want to measure things (especially outside the classroom). It works like a kit box.
2- Provision of opportunity for students to self explore the measurement materials before directed activities. However, guidance is still a necessity by giving questions like "I wonder if..." or "How many ways..". If students are able to produce or bring or think of an item to be measurement material, they should be used in classroom and shared among the class.
3- Directed activities are still prevalent but without too many instruction and rules which can limit their creativity and curiosity. Teachers should always give time for the students to explore and understand the concepts on their own as this will result in great insights.
Algebra: Balance
Do you know how object in the picture below works?
This is a scale. This object functions to measure the weight of any object. Back then, we found this a lot in shops to measure the weight of items that they sell. It employs the concept of balancing to know the weight.
In algebra, we have a term called balancing. Balancing refers to the process in which we attempt to balance two values. In mathematics, we use a lot of equation which obviously employ this concept. For example, 3x + 5 = 9 + 2x. The symbol '=' indicates that the first part (3x + 5) and the second part (9 = 2x) share the same value.
The understanding of this concept can assist young learners in accomplishing addition and subtraction problems, or any mathematical problems.
In the workshop, we 'played' with this object to visualize how we can solve addition and subtraction using balancing concept. Balancing concept claims that the two parts of the object should be in the same value or weight so that it will be balanced. Therefore, if we have 10 for one part, the other part should have ten.
For example, the question is:
4 + __ = 10
By understanding the concept of balancing, students can work on finding the question. On one part, they put the weight to be 10 'value' and the other part 4 'value'. So they have to count how many more 'value' to balance the scale.
Using this concept also help students knowing lots of ways to reach
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 I 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
part A middle part B
For example, if the students discover that in part A they have two fives (5 + 5), they should be able to reach to another equation of the same value. By retaining the value in part A and moving the value in part B, they should know that 4 + 6, 3 + 7, 2 + 8 and 1 + 9 are equal to 5 + 5.
4 + __ = 10
By understanding the concept of balancing, students can work on finding the question. On one part, they put the weight to be 10 'value' and the other part 4 'value'. So they have to count how many more 'value' to balance the scale.
Using this concept also help students knowing lots of ways to reach
part A middle part B
For example, if the students discover that in part A they have two fives (5 + 5), they should be able to reach to another equation of the same value. By retaining the value in part A and moving the value in part B, they should know that 4 + 6, 3 + 7, 2 + 8 and 1 + 9 are equal to 5 + 5.
Algebra: Function
Have you ever watched a magic show? There are times in a magic show that the magicians use an object such as box, table, hat or cloth to transform an object to become another object, a person with blue cloth to different type and colour of clothes.
from a bird
to become a rabbit
The object that the magicians use to transform an object/ a person to another thing works the same function as function in algebra.
Function (in algebra) works as a machine which can change a 'thing' to become another 'thing'. In the function, there is a rule that enable the function to operate.
Example follows:
Algebra: Introduction and Pattern
Algebra
Algebra is a branch of mathematics that uses mathematical statements to describe relationships between things that vary over time. Algebra is about finding the unknown or it is about putting real life problems into equations and then solving them (Rusell, 2010).
There are two patterns in algebra which are repeating and growing.
Repeating pattern refers to a sequence or set which is repeated over and over. Meanwhile, growing pattern is still a repetition of a set or sequence but in each repetition, there is an addition of any attributes e.g. quantity or shape.
There are five processes involved in pattern – recognize, copy, extend, create and translate. Recognizing a pattern is the process to detect the foundational idea in the pattern.
Copying a pattern refers to the process to detect the foundational idea and re-create, copy or describe a pattern.
When a pattern is extended, the set of elements is expanded to a larger set, and the rule is extended across the larger set.
Example:
In this example, from two block, the blocks extends to become four block, six blocks and eight blocks.
Create a pattern is the ability to come up with a new pattern using the same foundational idea and retaining the rule.
Translate a pattern refers to the ability to identify the rule and represent the pattern using different elements.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)


.jpg)





















